KNN คือ อะไร

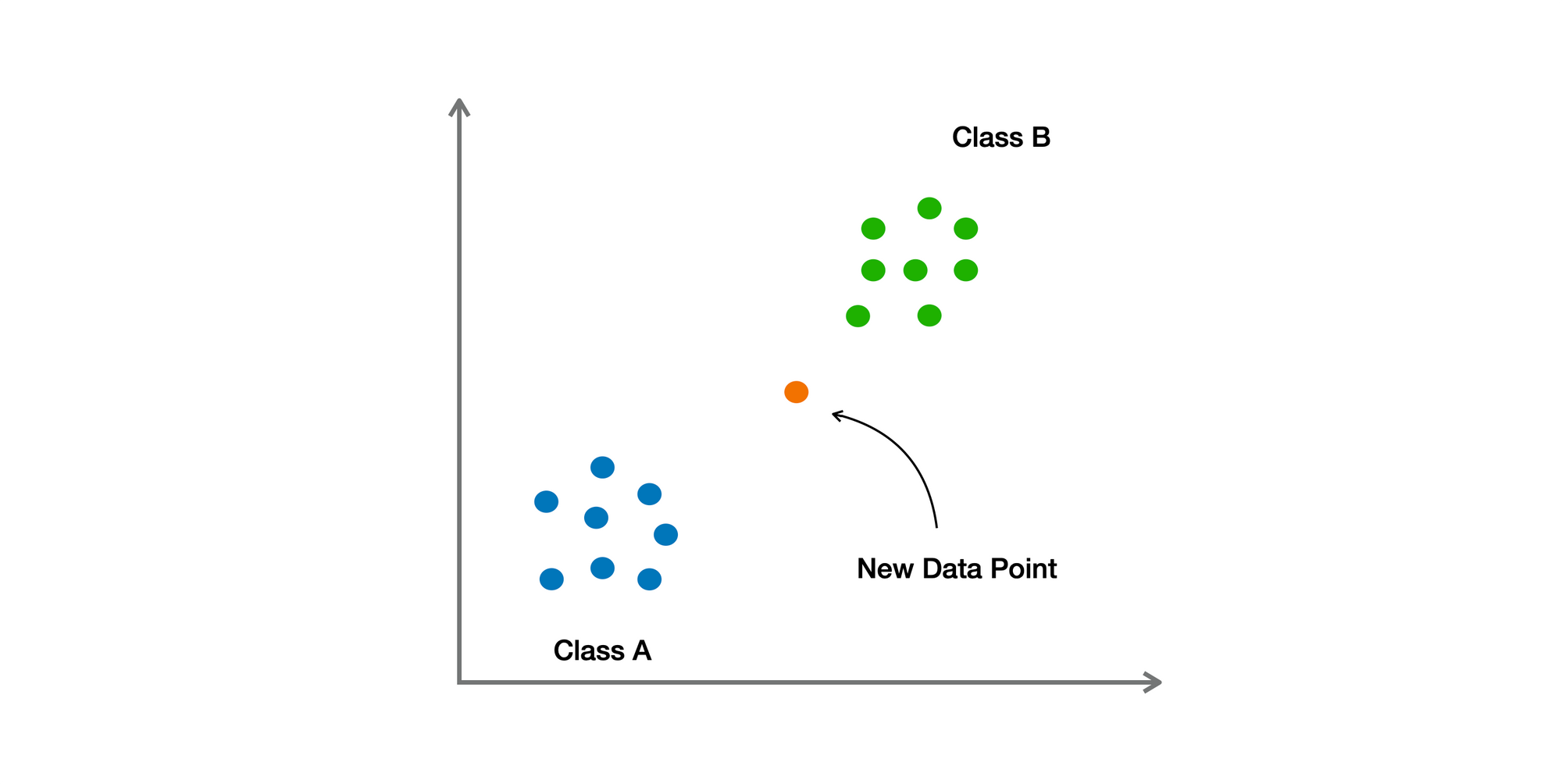
KNN ย่อจาก K-Nearest Neighbors ถือเป็น Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm ใข้ในการ Classification หรือ Regression ทำงานได้โดยการกำหนดค่า K ซึ่งก็คือ จำนวน Training Samples ที่มีระยะทางใกล้กับ Data Point ใหม่มากที่สุด และ ทำนายจาก Majority ของ K samples เหล่านั้น
❓ทำไมถึงใช้ KNN
- ความง่าย ในการ Implement
- ไม่ต้องมีกระบวนการ Training เริ่มที่กระบวนการ Prediction ได้เลย
- ปรับตัวได้ (Adaptive) ไม่จำเป็นต้องมีการ Re-training เมื่อมีข้อมูลใหม่เข้ามา
- สามารถใช้สำหรับ Non-Linear data และ กรณีที่เป็น Complex Boundaries ได้
- สามารถใช้ได้ทั้งปัญหา Classification และ Regression
🟢 ข้อดี
- ไม่ต้องมีสมมติฐานเกี่ยวกับ Function ที่เลือกมาใช้ ทำให้เหมาะกับทุกประเภทของข้อมูล
- เป็น Instance-based Learning ทำให้ง่ายในการปรับตัว
- รองรับปัญหาแบบ Multi-class Classification
🔴 ข้อเสีย
- ต้องมี Storage สำหรับ Dataset ทั้งชุด การหา Nearest Neighbors บางครั้งมีความซับซ้อนในการคำนวณที่มาก
- มีความไวต่อ Features ที่ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง เนื่องจากเป็นการคำนวณระยะทาง บางครั้ง Features ที่ไม่เกี่ยวข้องจะส่งผลต่อประสิทธิภาพของ Model ได้
- มีความไวต่อ Scale สำหรับ Features ที่มี Scale ที่สูงกว่า (ค่ามากกว่า) จะส่งผลต่อการคำนวณระยะทางที่มากกว่า
- ประสิทธิภาพลดลงหากเป็น High Dimensionality
Hyper-parameters ใน KNN
- จำนวนของ Neighbors (K)
- Distance Metrics (เช่น Euclidean, Manhattan, Minkowski)
- Wights (Uniform, Distance หรือ Custom)
- Algorithms (Brute-force, KD-Tree, Back Tree)
- Leaf Size (สำหรับ Tree-based Algorithms)
- P (Power Parameter สำหรับ Minkowski distance)
- Metric Params (Arguments เพิ่มเติม สำหรับ Metric Function)
ตัวอย่าง Python Code 👨🏻💻
# To import libraries
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
# To load iris dataset
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# To separate train and test data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# To define algorithm
KNN = KNeighborsClassifier()
# To define hyper-parameters
param_grid = {
'n_neighbors': np.arange(1,50),
'weights':['uniform','distance'],
'metric':['euclidean','manhattan','minkowski'],
'p':[1, 2, 3]
}
# To use grid search for hyper-paramter tuning
grid_search = GridSearchCV(KNN, param_grid, cv=5)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
# To print the best parameters
print ("Best Parameters: ", grid_search.best_params_)
# To use the best parameters for prediction
best_knn = grid_search.best_estimator_
y_pred = best_knn.predict(X_test)
# To print the accuracy and classification report (model's performance)
print ("Accuracy: ", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print (classification_report(y_test, y_pred))******
อ่านเพิ่มเติม Pros & Cons ของ Machine Learning Algorithms ที่นิยมใช้
******
ข้อมูลอ้างอิง - Analytics Vidhya