LSTM คือ อะไร

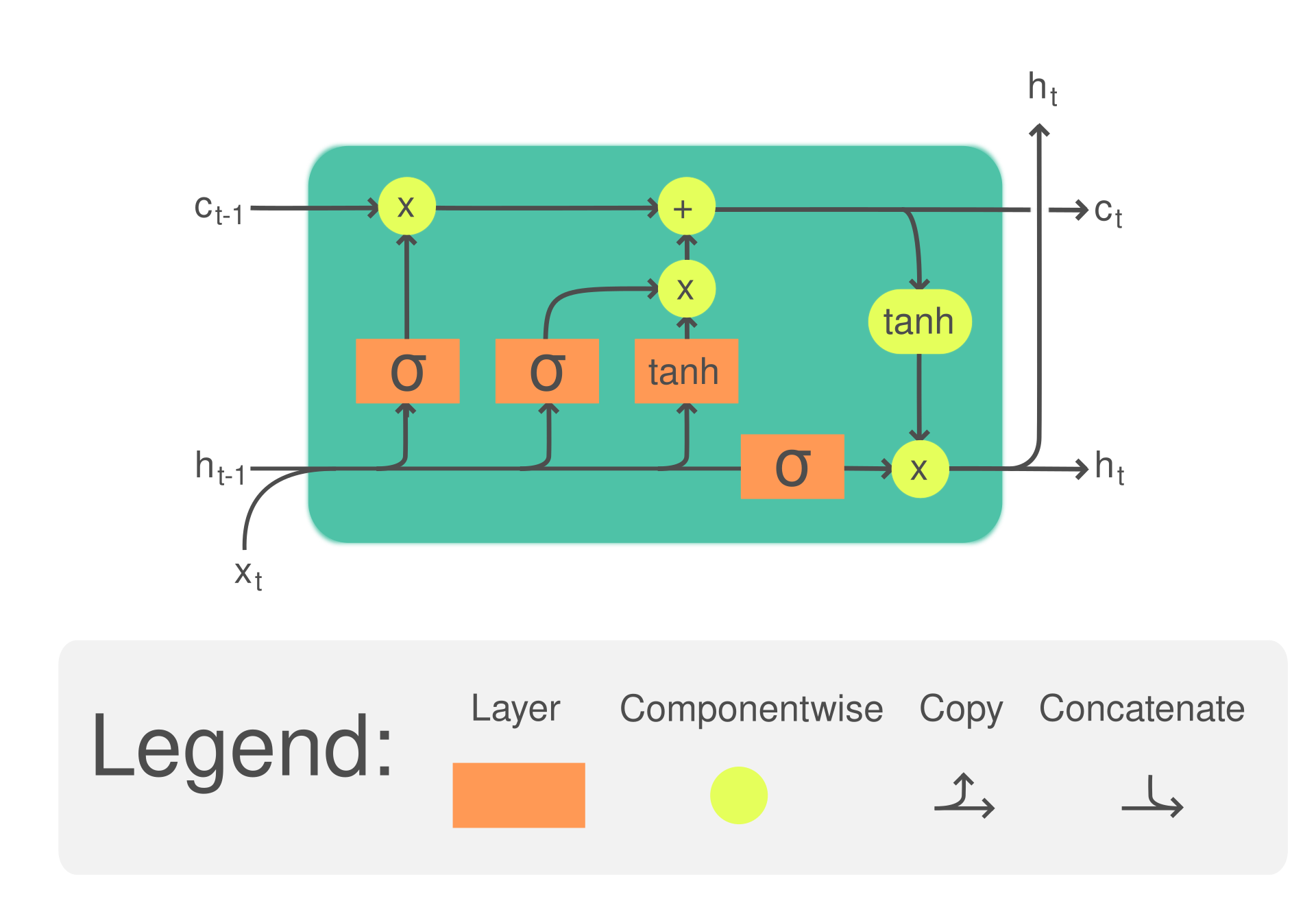
LSTM ย่อจาก Long Short-Term Memory ถือเป็นประเภทหนึ่งของสถาปัตยกรรมแบบ Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) อยู่ในกลุ่มของ Deep Learning
ถูกออกแบบให้จดจำ Patterns ในช่วงเวลานานๆ มีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับปัญหาการทำนายที่เป็น Sequential เนื่องจากสามารถเก็บข้อมูลก่อนหน้าและนำมาร่วมใช้ในการประมวลผลได้
สามารถแก้ปัญหา Long-term Dependency ได้ โดย RNN แบบดั้งเดิมจะเผชิญกับ ความท้าทายในเรื่อง Long-range Dependency และมีปัญหา Vanishing Gradient
LSTM ถูกออกแบบมาให้จดจำ Long-term Information โดยใช้ Gating Mechanisms ที่ออกแบบมาเฉพาะ
มีความยืดหยุ่นที่ดี LSTM สามารใช้ Model ได้ทั้ง Long-term และ Short-term Temporal Sequences
Applications
- Time-series Prediction เช่น การทำนายราคาหุ้น (Stock Prices Prediction) การทำนายยอดขาย (Sales Forecasting)
- NLP (Natural Language Processing) เช่น การ Generate text การทำ Sentimental Analysis การแปลภาษา
- Speech Recognition การแปลงภาษาพูด (Speech) ไปเป็นข้อความ (Text)
- Music Composition การสร้างเพลงใหม่ บนพื้นฐานของ Patterns ในอดีต
- Video Analysis การจำแนก Action หรือ Activities ใน Video Sequences
ข้อดี
- ความสามารถในการจดจำ การจดจำ Patterns จาก Long Sequences ทำให้เหมาะกับ Applications ส่วนใหญ่ในทางปฏิบัติ
- มีการนำไปใช้งานอย่างแพร่หลาย
- มี Libraries ต่างๆ รองรับ เช่น TensorFlow และ Keras ทำให้ง่ายต่อการ Implementation
ข้อเสีย
- ความซับซ้อนในการคำนวณ การ Train LSTMs ใช้เวลาและทรัพยากรในการคำนวณสูง
- ต้องใช้ Dataset จำนวนมาก สำหรับการ Train Model ที่มีประสิทธิภาพ และหลีกเลี่ยง Overfitting จำเป็นต้องใช้ Data จำนวนมาก
- Hyperparameter Tuning เหมือนกับ Neural Network อื่นๆ หากต้องการได้ประสิทธิภาพที่ดี จำเป็นต้องใช้ความพยายามกับการทำ Hyperparameter Tuning
ตัวอย่าง Python Code 👨🏻💻
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
# Create sample data
data = np.array([i for i in range(100)])
target = np.array([i for i in range(1, 101)])
# Reshape the data
data = data.reshape((100, 1, 1))
target = target.reshape((100, 1))
# Create a sequential model
model = Sequential()
# Add an LSTM layer with 50 units
model.add(LSTM(50, activation='relu', input_shape=(1, 1)))
# Add a dense (fully connected) layer with 1 unit for the output
model.add(Dense(1))
#Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse')
# Train the model
model.fit(data, target, epochs=300, validation_split=0.2, verbose=0)
# Predict a new value
test_input = np.array([100])
test_input = test_input.reshape((1, 1, 1))
test_output = model.predict(test_input)
print (test_output)
******
ข้อมูลอ้างอิง - Analytics Vidhya



